
Innovation excellence
FOCUS AREAS
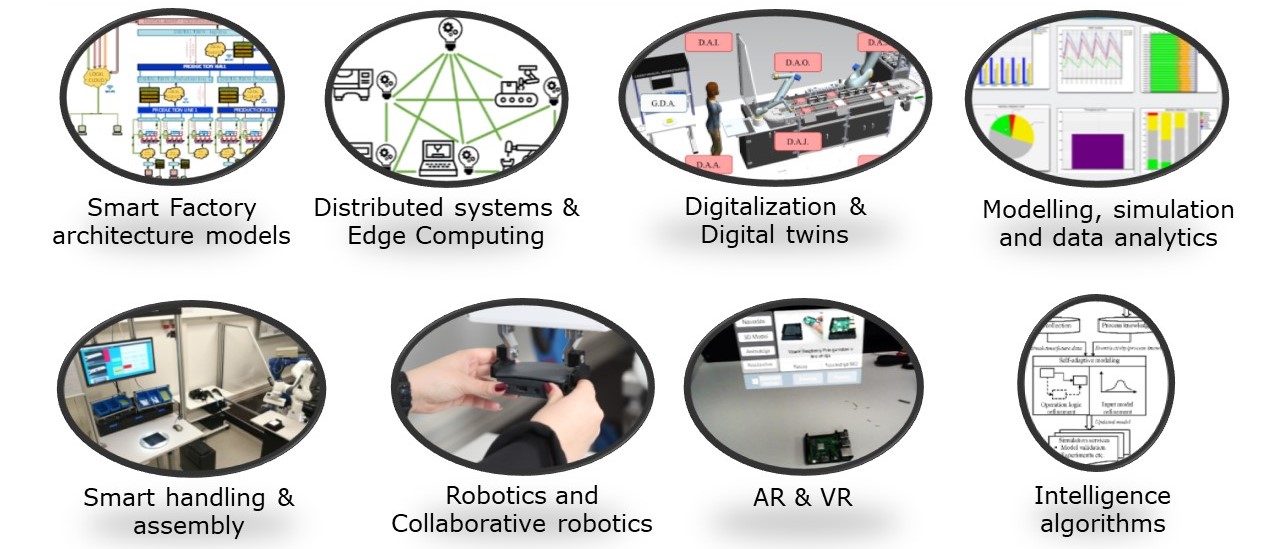
UL FME LASIM (University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, laboratory LASIM) expresses the innovation excellence through the fundamental R&D activities as well as applied research in different areas related to the factories of the future (FoF) and its key enablers. We are particular focused on intelligent manufacturing systems, automation, robotics as well as new control methods, algorithms and strategies. All the new technologies, mainly focused on the use of I4.0 principles are first analysed and validated in the laboratory environment and further on implemented into the real industrial environment and tested in the real industrial applications. The main R&I areas are:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main scientific and professional interest
In general, the core research and development areas of the LASIM laboratory and thus also of the experimental environment are:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main services
|
|
|
|
|
|
Significant infrastructure and equipment, Digital Factories
UL, FS, LASIM has all the necessary facilities for implementing the R&D activities, from human resources, to software and hardware. Beside R&D activities, we are specialized for trainings and education of human resources in the field of advanced manufacturing and smart automation. The main infrastructure of the laboratory presents Smart Factory Demo Lab and Agile Production and Logistic Demo Lab, where the new developed technologies can be tested, validated and prepared for the integration into the real industrial environment.
DF1 (Digital/didactic factory 1) - Smart Factory Demo Lab
The demo center is developed and built according to the principles of Industry 4.0 (I4.0) and provides the possibilities for basic and applied research of all key technologies I4.0 and logistics. The equipment includes a modern self-configurable production line, two industrial robots, one collaborative robot, automated smart rack warehouse, smart hydraulic servo press with integrated modular intelligent tools supported with digital twin technology to perform AGILE forming processes, machine vision technology on different locations, RFID technology and traceability, cloud technologies, 5G technology and edge computing, BIG Data technology (data capturing, processing and transferring and real-time data processing), digital twin’s technology of processes and digital agents (AI) at different levels (global, local, etc.), distributed production systems technology, VR and AR, smart and self-adaptive and self-configurable manual assembly workstation with LPM (LEAN Production Management system to cover the entire product life cycle and production value chain) system, supported by visualization, etc.
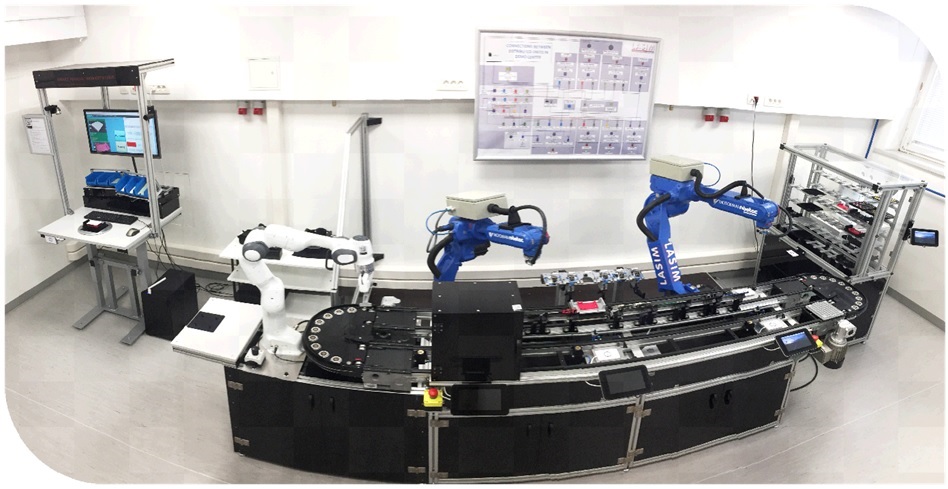

Figure: Smart Factory Demo Lab - digital twin technology integrated into production system VIDEO.
Key equipment and subsystems:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Testing services offered for digital and green technologies
|
Smart Factory Design Principles: Development, testing, and validation of new architectural models for the Factories of the Future (LASFA – LASIM Smart Factory Architecture) suitable for the Edge Computing approach and the integration over LAN, WiFi and 5G technology; Development, testing, and validation of new distributed production system concepts (Edge Computing); Development of digitalisation of legacy software to work in connected production systems of Smart Factories. |
|
Connectivity, Communication, and Data Transfer Approaches: Design, test, and validation of communication and data transfer in production and logistics processes, in combination with LAN, WiFi and 5G technology; Testing, validation and integration of communication protocols (OPC UA, Modbus, MQTT, EtherCAT, AMQP, CoAP,...); Design, test, and validation of communication and data transfer in production and logistics processes, in combination with LAN, WiFi and 5G technology; Testing, validation and integration of communication protocols (OPC UA, Modbus, MQTT, EtherCAT, AMQP, CoAP,...). |
|
Digitalization, Digital Twins Development, and Visualization:Development, testing, and validation of AI in digital twins of manufacturing processes including logistics; Development, testing, and validation of AI-based algorithms in relation to digital twins and digital agents; Development of Digital Twins with AI for real-time worker guidance and work activities distribution; HMI/GUI design and development to achieve efficient process monitoring. |
Description of the support offered to manufacturing companies before, during and after the testing phase
The process for companies to access the testing facilities: Our services are available within a controlled laboratory environment located in University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, laboratory LASIM, Aškerčeva 6, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia. Companies interested in utilizing our facilities should contact us via email (niko.herakovic@fs.uni-lj.si or marko.simic@fs.uni-lj.si), specifying their area of interest. A tailored workshop or testing session will then be organized to meet their specific needs.
How the center support companies throughout the testing process? The center provides comprehensive support throughout the testing process, starting with a live presentation and demonstration of the relevant technologies. Depending on the service, we also offer in-depth analysis of parameter adjustments and technology configurations for a deeper understanding. Compatibility with the company's processes is assessed, and we can collaborate on the integration of technologies and solutions as a final step.
Are there opportunities for companies to consult with technical experts? Consultation is possible and is internally organized during an all areas with different experts that work in laboratory LASIM.
Networking events available for companies to connect with potential partners or clients: We organize the annual ASM Conference (posvet-asm.si), which attracts over 150 partners, offering valuable networking opportunities. Additionally, other events are regularly posted on the event schedule available on the LASIM website (https://web.fs.uni-lj.si/lasim/index.php?page=home), providing further platforms for companies to connect with potential partners or clients.
SUCCESS STORIES AND CASE STUDIES
YASKAWA Europe Robotics d.o.o. significantly benefited from the implementation of our Digital Twin and Visualization solutions in two key areas. Through targeted education on Digital Twin usage, followed by the development of a tailored Digital Twin for planning a new robot production facility, the company achieved a remarkable 60% reduction in the required factory floor space, compared to facilities in Japan with similar production rates. This optimization also resulted in multimillion-euro savings on factory construction costs. The Digital Twin served as a comprehensive tool for optimizing the entire value chain, from Just-In-Time (JIT) parts ordering, warehouse sizing, CNC scheduling, and manual assembly line integration, to painting and testing processes.
Additionally, similar Digital Twin solutions have been successfully implemented in other companies, including Krka d.d. (warehouse layout optimization), ECOLAB d.o.o., SCANIA, IMP Armature d.o.o. and many others.
The developed LPM system, which can be tested in our laboratory, seamlessly connects the development department with the production line by restructuring the 3D product model into an assembly-focused structure tailored for manual worker guidance. This system has been successfully implemented at Yaskawa Ristro d.o.o., where it has become a critical tool for guiding assembly workers and preparing required materials in advance. The LPM system has reduced robot cell assembly and testing time by 40%, while also enabling the company to achieve near 100% traceability across manual assembly stations.
An advanced Digital Twin system with AI for real-time worker guidance was developed for Adria Dom d.o.o. This solution integrates ERP data and worker availability to dynamically plan the manual assembly of mobile homes. Leveraging advanced IT connectivity, the system connects the ERP, Digital Twin, and smartwatches with a visualization app, ensuring seamless communication across all platforms. The assembly plan is updated every three minutes based on real-time data from completed processes, worker expertise, and other operational metrics. Workers use smartwatches to log in, receive current tasks, and send updates upon task completion, enhancing efficiency and workflow management. Similar Digital Twin for planning without smart watches was implemented in company IMP Armature d.o.o.
DF2 (Digital/didactic factory 2) - Agile production and logistic Demo Lab
An agile, modular production line enables fast and easy reconfiguration through plug-and-play and self-recognition capabilities. It consists of mobile production modules, including AGVs and AMRs, each functioning as a Cyber-Physical Production System (CPPS) with integrated local digital twins, EDGE technology, and connectivity.
The modules interact based on input factors—such as energy, data, resources, materials, and technological constraints—and output factors—such as products, semi-finished goods, data, assets, and waste. Connected modules form flexible production processes that are controlled through a combination of local and global digital twins, merging global orchestration with local edge computing.
In the DF2 setup, eight different production modules are used for assembly, handling, warehousing, quality control, and material tracking. The system supports the analysis of different material and information flows by enabling reconfigurable layouts and varying sequences of production modules.
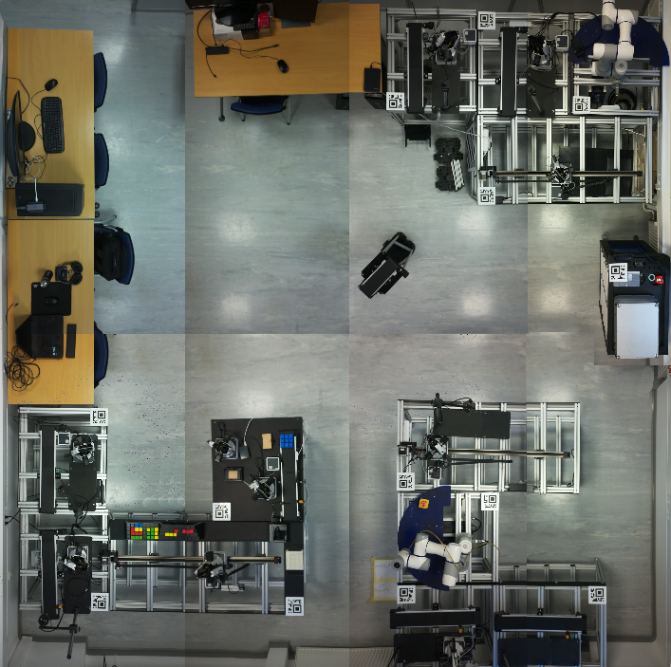

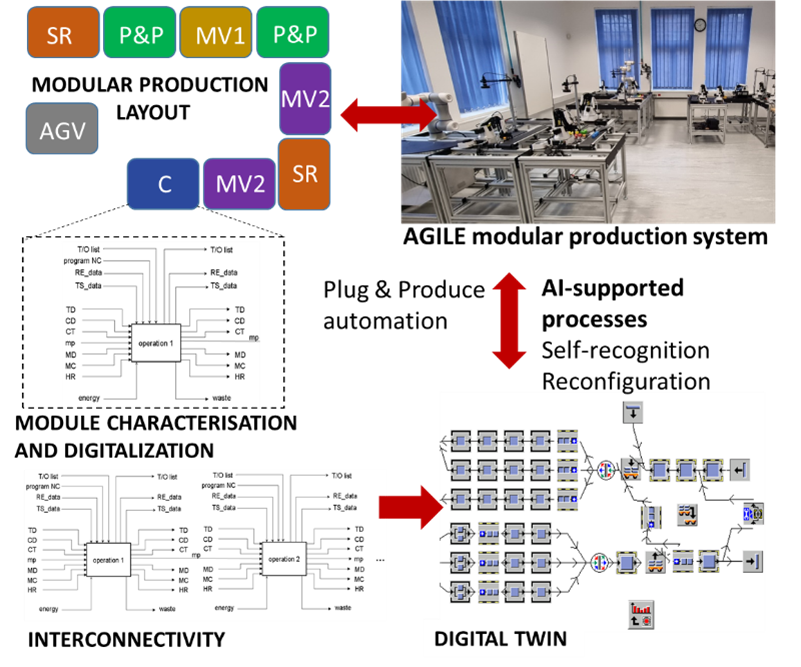
Figure: Modular production for agile production processes (8-camera view of production layout).
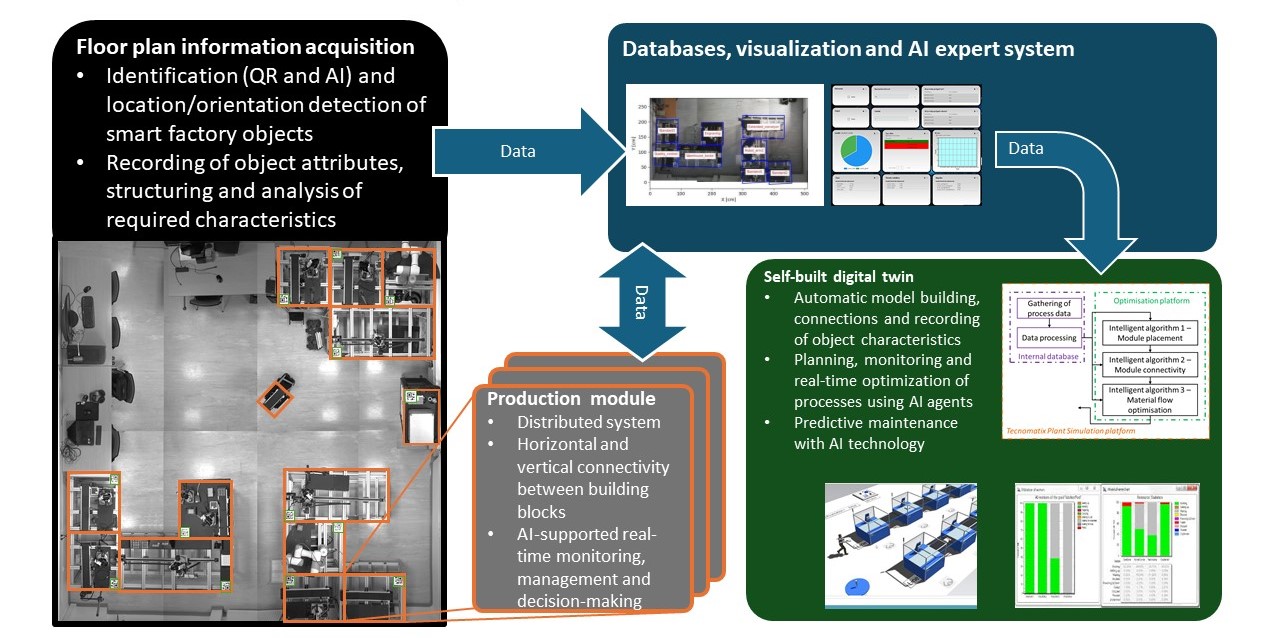
Figure: Production modules recognition by machine vision system and creation of virtual models.
More than 20 production modules (8 different types) are used to form different production layouts for different processes (based on different products and production plan):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Testing services offered for digital and green technologies
|
Smart modular self-aware and self-recognition production lines: Designing, testing, and validation of new modular production lines, analysing and evaluation of plug-and-produce principles, analysing and evaluation of different recognition principles (recognition of production modules location and orientation in production hall). Designing the global Administrative shells for production modules (characteristics, attributes, cloud data preparation, connectivity, error handling and maintenance). Development, testing, and validation of new distributed production system concepts (Edge Computing). Designing the Administrative shells for different production modules (digitalization, attributes and characteristics definition, designing the information structure). Testing and integration of AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robots) developed inhouse (using development hardware and ROS architecture) and finished industrial solutions with aim to test different sensors for detecting AMR orientation, track planning and obstacle avoidance and positioning. The mentioned services are performed in laboratory environment, the research results are available for demonstration.
|
|
Connectivity, Communication, and Data Transfer Approaches: Development, testing, and validation of connectivity, communication and data transfer in production and logistics processes. Designing, testing, and validation of communication protocols (OPC UA, MQTT, Modbus, ...). Designing, testing, and validation of HMIs, visualization and monitoring principles. The services are performed in laboratory environment, the research results are available for demonstration.
|
|
Digitalization, Digital Twins Development, and Visualization: Development, testing, and validation of AI in digital twins of logistics processes. Development, testing, and validation of AI-based digital agents. Development, testing, and validation of AI-based algorithms in relation to digital twins. HMI design and development to achieve efficient process monitoring. Daily energy consumption forecasting, real-time visualization, forecasting daily or even yearly energy consumption, optimizing energy procurement by enabling the purchase of the exact required amount in advance, thus reducing costs. The services are performed in laboratory environment, the research results are available for demonstration.
|
Description of the support offered to manufacturing companies before, during and after the testing phase
The process for companies to access the testing facilities: Our services are available within a controlled laboratory environment located at University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, laboratory LASIM, Aškerčeva 6, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia. Companies interested in utilizing our facilities should contact us via email (niko.herakovic@fs.uni-lj.si or marko.simic@fs.uni-lj.si), specifying their area of interest. A tailored workshop or testing session will then be organized to meet their specific needs. Online access point is currently under preparation.
How the center support companies throughout the testing process? The center provides comprehensive support throughout the testing process, starting with a live presentation and demonstration of the relevant technologies. Depending on the service, we also offer in-depth analysis of parameter adjustments and technology configurations for a deeper understanding. Compatibility with the company's processes is assessed, and we can collaborate on the integration of technologies and solutions as a final step.
Are there opportunities for companies to consult with technical experts? Consultation is possible and is internally organized during an all areas with different experts that work in laboratory LASIM.
Networking events available for companies to connect with potential partners or clients. We organize the annual ASM Conference (posvet-asm.si), which attracts over 150 partners, offering valuable networking opportunities. Additionally, other events are regularly posted on the event schedule available on the LASIM website (https://web.fs.uni-lj.si/lasim/index.php?page=home), providing further platforms for companies to connect with potential partners or clients.
SUCCESS STORIES AND CASE STUDIES
Based on the connectivity and visualization technologies developed within the DF2 project, we successfully integrated a daily energy consumption forecasting and metering system for IMP Armature d.o.o. The existing Digital Twin, used for production planning, was enhanced with energy consumption data from production machines, enabling precise energy usage calculations at 15-minute intervals. The machines were upgraded with energy consumption measurement devices, and the developed platform collects this data using MQTT and REST API communication protocols. This system provides real-time visualization, allowing the company to forecast daily or even yearly energy consumption, optimizing energy procurement by enabling the purchase of the exact required amount in advance, thus reducing costs.
Other equipment and software
|
HPC - high performance computer system to perform advanced simulation and real time optimization.
|
|
Siemens Plant Simulation – development of 2D and 3D digital models of the production lines and factories in order to simulate and optimize production process, material flow and logistics.
|
|
Siemens Process Simulate - modelling, simulation and visualization of manufacturing processes in combination with VR.
|
|
Visual Components – manufacturing simulation software for designing and simulation of factories.
|
|
Siemens Teamcenter – PLM-product lifecycle management.
|
|
GUI ThingsBoard platform – Open-source IoT platform (HMI/GUI development, real-time control, monitoring, visualization).
|
|
Beckhoff TwinCAT – PLC GUI, Windows based solution for PLC controllers.
|
|
VR/AR Unity engine – development tool for GUI development and animations of the systems.
|
|
MathLab, Simulink, Phython, C++ - programming, development of advanced control and decision-making algorithms.
|
|
NI LabVIEW software and hardware equipment – programming, experimental testing, GUI development in laboratory environment, test before invest, technology demonstration.
|
|
SolidWorks 3D CAD – digitalization of production systems and processes, pre-animation of production processes, 3D modelling of the components and systems, simple FEM analysis, simple CFD analysis.
|
|
DSHplus – modelling and simulation of pneumatic and hydraulic components and systems, hydraulic and pneumatic systems and processes optimization using what if scenarios and optimization methods.
|